A Pain In The Neck Là Gì
What is the prostate?
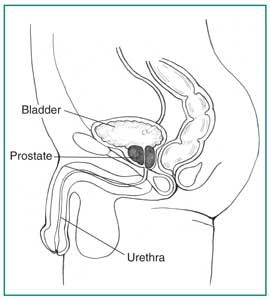
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gl& that is part of the male reproductive sầu system. It has two or more lobes, or sections, enclosed by an outer layer of tissue. The prostate is located in front of the rectum & just below the bladder, where urine is stored. It surrounds the urethra at the neck of the bladder & supplies fluid that goes into semen.
Bạn đang xem: A pain in the neck là gì
What are some comtháng prostate problems?
The most comtháng prostate problem in men younger than age 50 is inflammation, called prostatitis. Prostate enlargement, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is another common problem. Because the prostate continues to grow as a man ages, BPH is the most comtháng prostate problem for men older than age 50. Older men are at risk for prostate cancer as well, but it is much less common than BPH.
What are the symptoms of prostate problems?
The symptoms of prostate problems may include
urinary frequency—urination eight or more times a day urinary urgency—the inability to lớn delay urination nocturia—frequent urination at night trouble beginning a urine stream weak or interrupted urine stream blockage of urine urine that has an unusual color or odor pain after ejaculation or during urinationDifferent prostate problems may have sầu similar symptoms. For example, one man with prostatitis và another with BPH may both experience urinary urgency. Sometimes symptoms for the same prostate problem differ amuốn individuals. For example, one man with BPH may have sầu trouble beginning a urine stream, while another may experience nocturia. A man in the early stages of prostate cancer may have no symptoms at all. Because of this confusing array of symptoms, a thorough medical exam và testing are vital.
How are prostate problems diagnosed?
To diagnose prostate problems, the health care provider will perform a digital rectal exam (DRE). The health care provider will also ask the patient
when the problem began & how often it occurs what symptoms are present what medications he takes, both prescription và those bought over the counter the amount of fluid he typically drinks each day whether he consumes caffeine and alcohol about his general medical history, including any major illnesses or surgeriesAnswers to lớn these questions will help the health care provider identify the problem or determine what medical tests are needed. Diagnosing BPH may require a series of medical exams and tests.
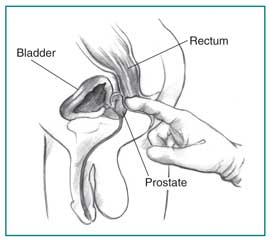
How is a digital rectal exam (DRE) performed?
A DRE is a physical exam of the prostate. The health care provider will ask the patient khổng lồ bkết thúc over a table or lie on his side while holding his knees close to his chest. The health care provider slides a gloved, lubricated finger inkhổng lồ the rectum và feels the part of the prostate that lies next to it. The DRE may be slightly uncomfortable, but it is brief. This exam reveals whether the prostate has any abnormalities that require more testing. If an infection is suspected, the health care provider might mas sa the prostate during the DRE lớn obtain fluid lớn examine with a microscope. This exam is usually done first. Many health care providers perkhung a DRE as part of a routine physical exam for men age 50 or older, some even at age 40, whether or not the man has urinary problems.
What is the first chạy thử for detecting prostate problems?
The first demo for detecting prostate problems is a blood demo to lớn measure prostate-specific antigene (PSA), a protein made only by the prostate gland. This test is often included in routine physical exams for men older than age 50. Because African American men have higher rates of getting, và dying from, prostate cancer than men of other racial or ethnic groups in the United States, medical organizations recommkết thúc a PSA blood test be given starting at age 40 for African American men. Medical organizations also recommkết thúc a PSA blood kiểm tra be given starting at age 40 for men with a family history of prostate cancer. Some medical organizations even recommend a PSA blood kiểm tra be given lớn all men starting at age 40.
If urination problems are present or if a PSA blood kiểm tra indicates a problem, additional tests may be ordered. These tests may require a patient khổng lồ change his diet or fluid intake or lớn stop taking medications. If the tests involve sầu inserting instruments inkhổng lồ the urethra or rectum, antibiotics may be given before & after the test lớn prevent infection.
Why is a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test performed?
A PSA blood kiểm tra is performed to lớn detect or rule out prostate cancer. The amount of PSA in the blood is often higher in men who have sầu prostate cancer. However, an elevated PSA cấp độ does not necessarily indicate prostate cancer. The U.S. Food & Drug Administration has approved the PSA blood kiểm tra for use in conjunction with a DRE to help detect prostate cancer in men age 50 or older & for monitoring men with prostate cancer after treatment. However, much remains unknown about how lớn interpret a PSA blood demo, its ability lớn discriminate between cancer và problems such as BPH và prostatitis, và the best course of action if the PSA level is high.
When done in addition to a DRE, a PSA blood kiểm tra enhances detection of prostate cancer. However, the thử nghiệm is known to lớn have relatively high false-positive sầu rates. A PSA blood demo also may identify a greater number of medically insignificant lumps or growths, called tumors, in the prostate. Health care providers và patients should weigh the benefits of PSA blood testing against the risks of follow-up diagnostic tests. The procedures used lớn diagnose prostate cancer may cause significant side effects, including bleeding & infection.
What are additional tests for detecting prostate problems?
If the DRE or the PSA blood thử nghiệm indicates a problem may exist, the health care provider may order additional tests, including urinalysis, urodynamic tests, cystoscopy, abdominal ultrasound, transrectal ultrasound with prostate biopsy, và imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) scan.
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the testing of a urine sample for abnormal substances or signs of infection. The urine sample is collected in a special container in a health care provider’s office or commercial facility và can be tested in the same location or sent lớn a lab for analysis.
If an infection is suspected, the health care provider may ask that the urine sample be collected in two or three containers during a single urination lớn help locate the infection site. After the first collection, the health care provider will have sầu the patient stop the urine stream for a prostate mas sa before collecting more urine. If signs of infection appear in the first container but not in the others, the infection is likely to lớn be in the urethra. If the urine contains significantly more bacteria after the prostate massage or bacteria are in the prostate fluid itself, the infection is likely to be in the prostate.
Urodynamic Tests
Urodynamic testing is any procedure that looks at how well the bladder, sphincters, & urethra are storing & releasing urine. Most urodynamic tests focus on the bladder’s ability lớn hold urine và empty steadily và completely. If the prostate problem appears lớn be related to lớn urine blockage, the health care provider may recommover tests that measure bladder pressure và urine flow rate. One thử nghiệm involves urinating into a special device that measures how quickly the urine is flowing và records how many seconds it takes for the peak flow rate to be reached. Another chạy thử measures postvoid residual, the amount of urine left in the bladder when urination stops. A weak urine stream & urinary retention may be signs of urine blockage caused by an enlarged prostate that is squeezing the urethra. Some urodynamic tests are performed in a health care provider’s office without anesthesia. Other urodynamic tests are performed in a health care provider’s office, outpatient center, or hospital with local anesthesia.
Xem thêm: Cực Bất Ngờ Khi Bạn Biết Cung Bọ Cạp Hợp Màu Gì, Nên Chọn Loại Sổ Da Nào
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is a procedure that allows the health care provider to lớn look for blockage in the lower urinary tract. A cystoscope is a tubelượt thích instrument used to lớn look inside the urethra và bladder. After a solution numbs the inside of the penis, the health care provider inserts the cystoscope through the opening at the tip of the penis and into the lower urinary tract. By looking through the cystoscope, the health care provider can determine the location và degree of the urine blockage. A cystoscopy is performed in a health care provider’s office, outpatient center, or hospital with local anesthesia. The procedure is usually performed by a urologist, a doctor who specializes in treating problems of the urinary tract và the male reproductive sầu system.
Abdominal Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses a device, called a transducer, that bounces safe, painless sound waves off organs to lớn create an image of their structure. The transducer can be moved khổng lồ different angles khổng lồ make it possible to examine different organs. In abdominal ultrasound, the health care provider applies a gel to the patient’s abdomen and moves a handheld transducer over the skin. The gel allows the transducer to lớn glide easily, and it improves the transmission of the signals. The procedure is performed in a health care provider’s office, outpatient center, or hospital by a specially trained technician and interpreted by a doctor, usually a radiologist—a doctor who specializes in medical imaging. Anesthesia is not needed. An abdominal ultrasound can create images of the entire urinary tract. The images can show damage or abnormalities in the urinary tract resulting from urine blockage at the prostate.
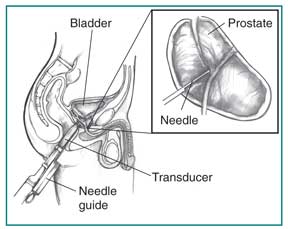
Transrectal Ultrasound with Prostate Biopsy
Transrectal ultrasound is most often used to examine the prostate. In a transrectal ultrasound, the health care provider inserts a transducer slightly larger than a pen into lớn the man’s rectum next to the prostate. The ultrasound image shows the size of the prostate và any abnormal-looking areas, such as tumors. Transrectal ultrasound cannot definitively identify prostate cancer.
To determine whether a tumor is cancerous, the health care provider uses the transducer & ultrasound images to guide a needle to the tumor. The needle is then used khổng lồ remove a few pieces of prostate tissue for examination with a microscope. This process, called biopsy, can reveal whether prostate cancer is present. A transrectal ultrasound with prostate biopsy is usually performed by a doctor in a health care provider’s office, outpatient center, or hospital with light sedation và local anesthesia. The biopsied prostate tissue is examined in a laboratory by a pathologist—a doctor who specializes in diagnosing diseases.
MRI & CT Scan
An MRI is a kiểm tra that takes pictures of the body’s internal organs & soft tissues without using x-rays. The MRI machines use radio waves & magnets khổng lồ produce detailed pictures. An MRI may also involve sầu the injection of dye. A CT scan uses a combination of x-rays và computer technology khổng lồ create three-dimensional (3-D) images. A CT scan may also involve the injection of a dye. MRI and CT scan images can help identify abnormal structures in the urinary tract, but they cannot distinguish between cancerous tumors and noncancerous prostate enlargement. Once a biopsy has confirmed cancer, these imaging techniques will show how far the cancer has spread. MRIs and CT scans are usually performed at an outpatient center or hospital by a specially trained technician & interpreted by a radiologist; anesthesia is not needed. For an MRI, light sedation may be used for people with a fear of confined spaces.
What happens after the prostate tests?
Urodynamic tests and cystoscopy may cause mild discomfort for a few hours after the procedures. Drinking an 8-ounce glass of water every half-hour for 2 hours may help reduce discomfort. The health care provider may recommend taking a warm bath or holding a warm, damp washcloth over the urethral opening to lớn relieve discomfort. A prostate biopsy may produce pain in the area of the rectum and the perineum, which is between the rectum và the scrotum. A prostate biopsy may also produce blood in urine và semen.
An antibiotic may be prescribed for 1 or 2 days to prsự kiện infection.
Patients with signs of infection—including pain, chills, or fever—should hotline their health care provider immediately.
How soon will prostate test results be available?
Results for simple medical tests such as some urodynamic tests, cystoscopy, and abdominal ultrasound are often available soon after the chạy thử. The results of other medical tests such as PSA blood chạy thử và prostate tissue biopsy may take several days to lớn come bachồng. A health care provider will talk with the patient about the results và possible treatments for the problem.
Eating, Diet, & Nutrition
Eating, diet, and nutrition have not been shown khổng lồ play a role in causing or preventing prostate problems.
Clinical Trials
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive sầu & Kidney Diseases (kinhnghiemdanhbac.com) and other components of the National Institutes of Health (kinhnghiemdanhbac.com) conduct & support retìm kiếm inlớn many diseases & conditions.
What are clinical trials, & are they right for you?
Clinical trials are part of clinical research & at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways lớn prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the unique of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
Xem thêm: Trước Khi Trở Thành Cô Trò, Khánh Thi & Nữ Chính "Người Ấy Là Ai" Đều Là Bạn Gái Cũ Của Kiện Tướng Dance Sport Chí Anh
What clinical trials are open?
Clinical trials that are currently open & are recruiting can be viewed at www.ClinicalTrials.gov.



















